Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can cause this condition. It is diagnosed in patients who do not play tennis when the use of the elbow mimics repetitive motion similar to the tennis activity.
The cause of pain is this condition is the inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow. The forearm muscles and tendons become damaged from overuse. Patients present with tenderness on the outside of the elbow and occasionally the pain travels to the forearm.
There are a lot of treatments for tennis elbow, more than 10-15 and the reason is that none of them has been found to cure the problem fast or consistently in all patients. Generally, the treatment begins the physical therapy
The muscles that control the extensor of the wrist originated from the same area on the outside part of the elbow, known as the common extensor origin. See picture below
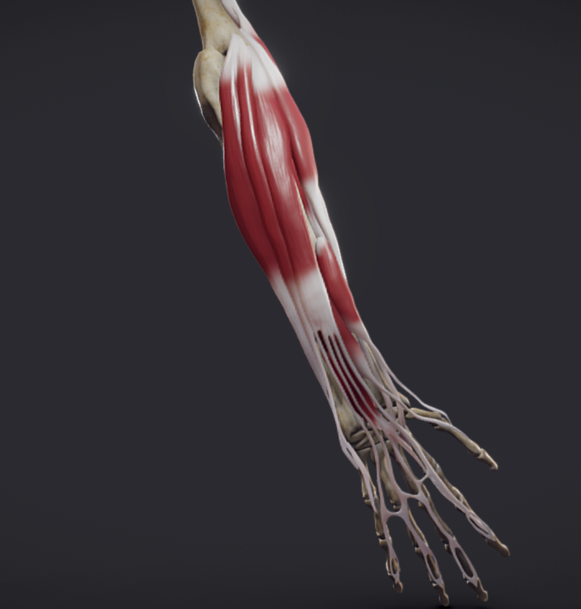
Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow, involves the muscles and tendons of your forearm. Your forearmmuscles extend your wrist and fingers. Your forearm tendons — often called extensors — attach the muscles to bone. They attach on the lateral epicondyle. The tendon usually involved in tennis elbow is called the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (ECRB).
Cause
Overuse: In tennis elbow the ECRB is weakened from overuse, microscopic tears form in the tendon where it attaches to the lateral epicondyle. This leads to inflammation and pain.
Activities: Athletes are not the only people who get tennis elbow. Many people with tennis elbow participate in work or recreational activities that require repetitive and vigorous use of the forearm muscle.
Painters, plumbers, and carpenters are particularly prone to developing tennis elbow. Studies have shown that auto workers, cooks, and even butchers get tennis elbow more often than the rest of the population. It is thought that the repetition and weight lifting required in these occupations leads to injury.
Age: Most people who get tennis elbow are between the ages of 30 and 50, although anyone can get tennis elbow if they have the risk factors. In racquet sports like tennis, improper stroke technique and improper equipment may be risk factors.
Unknown: Lateral epicondylitis can occur without any recognized repetitive injury. This occurence is called "insidious" or of an unknown cause.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tennis elbow develop gradually. In most cases, the pain begins as mild and slowly worsens over weeks and months. There is usually no specific injury associated with the start of symptoms.
Common signs and symptoms of tennis elbow include:
- Pain or burning on the outer part of your elbow
- Weak grip strength
The symptoms are often worsened with forearm activity, such as holding a racquet, turning a wrench, or shaking hands. Your dominant arm is most often affected; however both arms can be affected.
Doctor Examination
Your doctor will consider many factors in making a diagnosis. These include how your symptoms developed, any occupational risk factors, and recreational sports participation.
Your doctor will talk to you about what activities cause symptoms and where on your arm the symptoms occur. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have ever injured your elbow. If you have a history of rheumatoid arthritis or nerve disease, tell your doctor.
During the examination, your doctor will use a variety of tests to pinpoint the diagnosis. For example, your doctor may ask you to try to straighten your wrist and fingers against resistance with your arm fully straight to see if this causes pain. If the tests are positive, it tells your doctor that those muscles may not be healthy.
Tests
Your doctor may recommend additional tests to rule out other causes of your problem.
- X-rays These tests provide clear images of dense structures like bone. They may be taken to rule out arthritis of the elbow.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan If your doctor thinks your symptoms are related to a neck problem, an MRI scan may be ordered. MRIs scans show details of soft tissues, and will help your doctor see if you have a possible herniated disk or arthritis in your neck. Both of these conditions often produce arm pain.
-
Electromyography (EMG)
Your doctor may order an EMG to rule out nerve compression. Many nerves travel around the elbow, and the symptoms of nerve compression are similar to those of tennis elbow
Treatment
Approximately 80% to 95% of patients have success with nonsurgical treatment.
Rest. The first step toward recovery is to give your arm proper rest. This means that you will have to stop participation in sports or heavy work activities for several weeks.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. Drugs like aspirin or ibuprofen reduce pain and swelling.
Physical therapy. Specific exercises are helpful for strengthening the muscles of the forearm. Your therapist may also perform ultrasound, ice massage, or muscle- stimulating techniques to improve muscle healing.
Brace. Using a brace centered over the back of your forearm may also help relieve symptoms of tennis elbow. This can reduce symptoms by resting the muscles and tendons.

Steroid injections. Steroids, such as cortisone, are very effective anti-inflammatory medicines. Your doctor may decide to inject the painful area around your lateral epicondyle with a steroid to relieve your symptoms
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Shock wave therapy sends sound waves to the elbow. These sound waves create "microtrauma" that promote the body's natural healing processes. Shock wave therapy is considered experimental by many doctors, but some sources show it can be effective.
Equipment check. If you participate in a racquet sport, your doctor may encourage you to have your equipment checked for proper fit. Stiffer racquets and looser-strung racquets often can reduce the stress on the forearm, which means that the forearm muscles do not have to work as hard. If you use an oversized racquet, changing to a smaller head may help prevent symptoms from recurring.
Surgical Treatment
If your symptoms do not respond after 6 to 12 months of nonsurgical treatments, your doctor may recommend surgery Most surgical procedures for tennis elbow involve removing diseased muscle and reattaching healthy muscle back to bone.
The right surgical approach for you will depend on a range of factors. These include the scope of your injury, your general health, and your personal needs. Talk with your doctor about the options. Discuss the results your doctor has had, and any risks associated with each procedure.
Open surgery. The most common approach to tennis elbow repair is open surgery. This involves making an incision over the elbow.
Open surgery is usually performed as an outpatient surgery. It rarely requires an overnight stay at the hospital.
Arthroscopic surgery. Tennis elbow can also be repaired using miniature instruments and small incisions. Like open surgery, this is a same-day or outpatient procedure.
Surgical risks. As with any surgery, there are risks with tennis elbow surgery. The most common things to consider include:
- Infection
- Nerve and blood vessel damage
- Possible prolonged rehabilitation
- Loss of strength
- Loss of flexibility
- The need for further surgery
Rehabilitation. Following surgery, your arm may be immobilized temporarily with a splint. About 1 week later, the sutures and splint are removed.
After the splint is removed, exercises are started to stretch the elbow and restore flexibility. Light, gradual strengthening exercises are started about 2 months after surgery.
Your doctor will tell you when you can return to athletic activity. This is usually 4 to 6 months after surgery. Tennis elbow surgery is considered successful in 80% to 90% of patients. However, it is not uncommon to see a loss of strength.
New Developments
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is currently being investigated for its effectiveness in speeding the healing of a variety of tendon injuries. PRP is a preparation developed from a patient's own blood. It contains a high concentration of proteins called growth factors that are very important in the healing of injuries.